Gonorrhea
What is Gonorrhea?
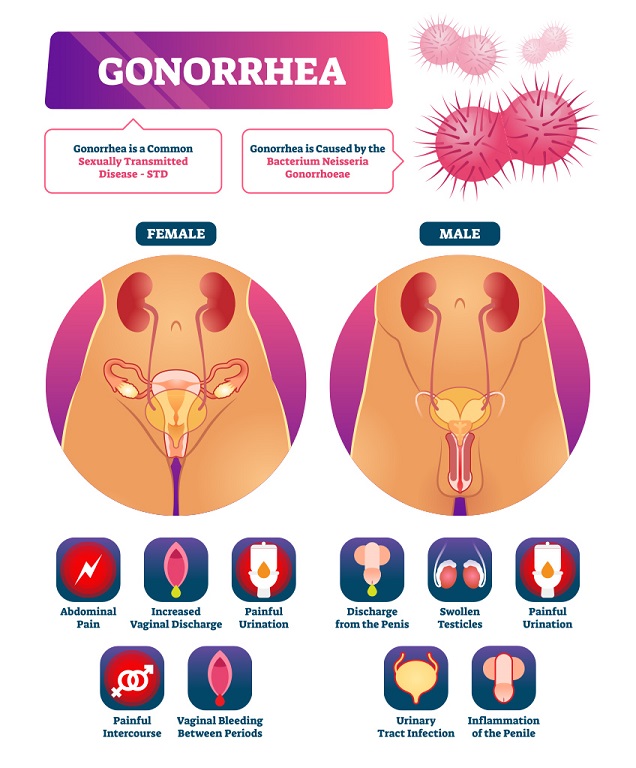
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria called Neisseria Gonorrheae or gonococcus. It used to be known as 'the clap'. It often occurs at the same time as chlamydia.
How does someone get gonorrhea?
- Anyone can get gonorrhea. It is very common and can be easily transmitted during vaginal, oral and anal sex.
- If you are pregnant and have Gonorrhea, you can pass the infection to your baby during childbirth.
- Often, this infection does not present with symptoms.
- You can pass Gonorrhea to others without knowing it.
- Gonorrhea can be treated and cured.
- If you do not treat Gonorrhea, it can lead to serious health problems.
- Even if you have had Gonorrhea before, you can still catch it again.
How can I lower my risk for Gonorrhea?
- Use condoms every time you have sex.
- Get tested as often as necessary.
- Limit your number of partners.
- Do not have sex if you are drunk or have used illicit drugs.
N.B. Washing the genitals after sex will not prevent STIs.
What are the symptoms of Gonorrhea?
You may not know that you have Gonorrhea but you may still be infected and pass the infection to other sexual partners. Most people who have Gonorrhea don't know it. However, you may experience:
Persons with female anatomical and physiological characteristics
- A change in colour (thick green, yellowish discharge), smell, or an increase in discharge from the vagina.
- Bleeding between periods.
- Pain or bleeding during or after vaginal sex.
- Burning sensation while urinating.
- Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Persons with male anatomical and physiological characteristics
- Burning sensation while urinating.
- Discharge from penis.
- Burning or itching around the opening of the penis.
- Pain in the testicles.
How can I find out if I have Gonorrhea?
- You can call the Genito-Urinary Clinic at Mater Dei Hospital (Out-patient's Level 2) on 25457494/1 for an appointment.
- The doctor will ask you for a urine sample and swabs may be taken from the throat, cervix, anus or penis.
- You may get tested for other STIs as one can have other sexually transmitted infections at the same time.
When should I be tested?
- You should be tested as soon as you experience any of the symptoms.
- If you had or are having unprotected vaginal, anal or oral sex.
- If you had or are having unprotected sex with more than one partner.
The bacteria are mainly found in discharge from the penis and in vaginal fluid.
How is Gonorrhea treated?
- Gonorrhea can be treated and cured with antibiotics.
- Make sure to finish all medicines. Do not share them with others.
- The doctor will inform you when you can be sexually active again. It is important that you do not have sex until the completion of the medicines. Follow your doctor’s advice. The duration of treatment will affect the timing of when you can have sex again.
- It is important to tell your doctor if you are pregnant as you will need different antibiotics.
What are the complications of Gonorrhea, if I don’t get treated?
In persons with female anatomical and physiological characteristics
Gonorrhea may spread internally up to the pelvic floor causing an infection - a condition known as Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). PID can lead to scarring of the Fallopian tube causing ectopic pregnancy and/or infertility.
In persons with male anatomical and physiological characteristics
Gonorrhea can spread from the urethra to the testicles and cause pain. This may very rarely lead to fertility problems.
It can lead to serious infection in the blood called septicaemia. However, if treated early, all complications can be prevented.
Do I have to inform my partner about Gonorrhea?
- Your partner may have Gonorrhea too.
- Be sure to tell your recent sex partners so that they can get tested and treated. They may have it too without knowing it.
- Healthcare professionals may help you in notifying your sexual partners in a confidential manner.
- If someone shares their sexual health status with you be thankful - don’t shame them. You and your partner can get tested and treated!
Can I get Gonorrhea again after I’ve been treated?
Yes, you can get Gonorrhea again. You can get it from an untreated sexual partner.
Gonorrhea and pregnancy
The infection can also be passed from a pregnant person to her baby during childbirth. If you're pregnant and are at risk of being infected with Gonorrhea, it's important to get tested and treated before your baby is born.
Without treatment, Gonorrhea can cause permanent blindness, joint infection, or life-threatening blood infection in a newborn baby.
Does Gonorrhea affect my risk of getting HIV?
Yes, Gonorrhea increases the risk of getting infected with HIV.
How can Gonorrhea be prevented?
Gonorrhea and other STIs can be successfully prevented by using appropriate contraception and by taking other precautions, such as:
- Using male condoms or female condoms each time you have vaginal sex, or male condoms during anal sex.
- Using a condom to cover the penis, or a latex or plastic square (dam) to cover the female genitals if you have oral sex.
- Not sharing sex toys, or washing them before and after sex and covering them with a new condom before anyone else uses them.
Further information and help
Reference List:
https://iusti.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Gonorrhoea2019.pdf
https://www.bashhguidelines.org/media/1129/gonorrhoea-screen.pdf