Hepatitis B & D
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. There are different types of Hepatitis, but this fact sheet will only focus on Hepatitis B and D.
What is Hepatitis B?
The Hepatitis B virus causes a liver infection which can be acute or chronic. Acute Hepatitis B is when a person has been infected for less than 6 months, with symptoms varying from no symptoms, to mild, to severe, requiring admission to hospital. Some people clear the virus, hence becoming immune and unable to catch the disease again. Acute Hepatitis B can lead to chronic Hepatitis B. The risk for a person to develop chronic infection depends on the age of the person when they become infected. The younger the infected person, the more likely they are to develop chronic infection. Circa 90% of infants infected with Hepatitis B will develop chronic infection, whereas 2-6% of adults will develop chronic Hepatitis B infection. Chronic infection lasts longer than 6 months and lasts for one’s entire life. Chronic Hepatitis B can lead to serious health problems, including: liver damage, cirrhosis (the liver will be inflamed, the cells will degenerate, and there will be fibrous thickening of the liver tissue), liver cancer, and possible death.
What is Hepatitis D?
The Hepatitis D virus only occurs in individuals infected with the Hepatitis B virus. This is because it is an incomplete virus and needs the helper function of the Hepatitis B virus to replicate. This can lead to both acute and chronic infections. People who have chronic Hepatitis B and D infections develop complications more often and more quickly than those with chronic Hepatitis B infection alone.
What are the symptoms of Hepatitis B and D?
Symptoms of Hepatitis B vary a lot from mild to severe, and usually occur between 1 to 4 months after infection. Children may have no symptoms at all. Symptoms include: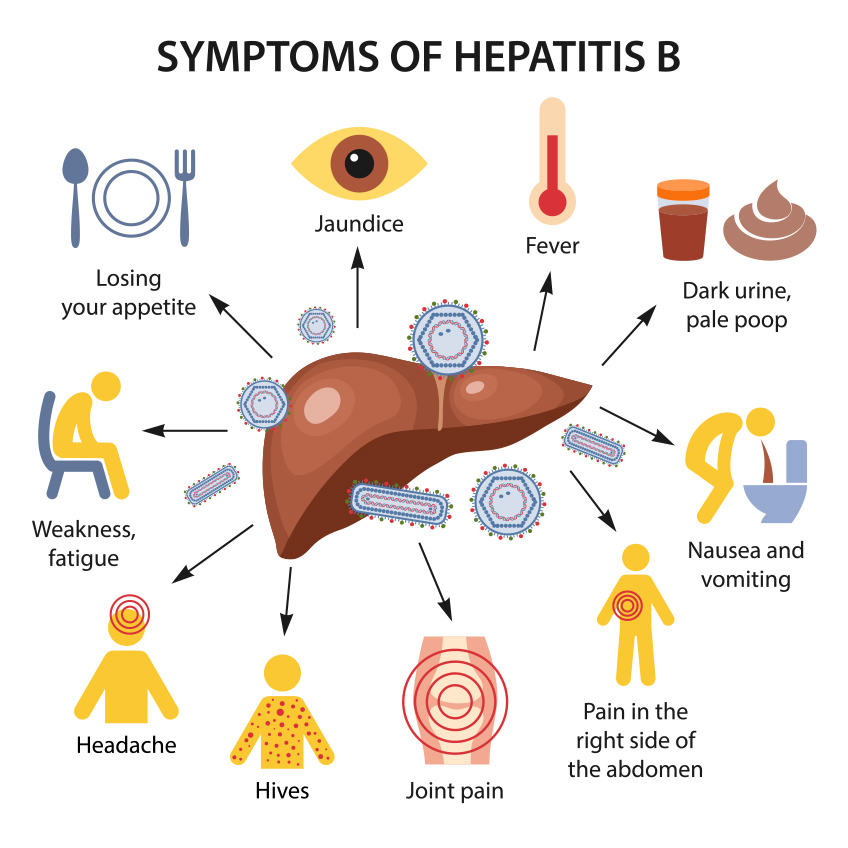 What is the duration of symptoms in Hepatitis B?
What is the duration of symptoms in Hepatitis B?
This depends on whether the infection is acute or chronic.
- Acute Hepatitis B infection lasts less than 6 months.
- Chronic Hepatitis B infection lasts 6 months or longer. It lingers because your immune system can't fight off the infection. This may last a lifetime, resulting in cirrhosis and liver cancer.
What is the duration of the symptoms of Hepatitis D?
Acute hepatitis occurs when there is simultaneous infection with Hepatitis B and D viruses, leading to a mild-to-severe or even fulminant hepatitis, but recovery is usually complete and development of chronic Hepatitis D is rare (less than 5% of acute hepatitis).
Superinfection occurs when Hepatitis D infects a person already chronically infected with Hepatitis B virus. The superinfection accelerates progression to a more severe disease in all ages and in 70‒90% of persons. It also accelerates progression to cirrhosis almost a decade earlier than Hepatitis B infection alone, even though it suppresses Hepatitis B replication.
Are there different types of Hepatitis B and D?
There are 4 types of Hepatitis B, known as genotypes, classified as A to D. Genotype D is the most common in Southern Europe.
There are 8 genotypes of Hepatitis D, classified as 1 to 8. Genotype 1 is the most common in the western world. This has an increased risk of liver failure when compared to Hepatitis B.
How is the Hepatitis B virus spread?
- Mother-to-child transmission (most common).
- Contact with infected blood or body fluids.
- Unprotected intercourse with an infected person.
- Sharing needles to inject drugs.
- Needlestick injuries.
- Infected household member.
Who is at risk of infection?
Hepatitis B can affect any age group:
- Sex partners of infected individuals.
- Men who have sex with men (MSM).
- Household contacts of infected people.
- Healthcare providers.
- People living with HIV infection.
Is there treatment?
- Hepatitis B Immunoglobulins should be given within 12 hours of exposure.
- If it is determined that you suffer from acute infection, you may require no treatment.
- If there is chronic infection there may be need for treatment for the rest of a person’s life. This can be discussed further with your doctor.
How can it be prevented?
The best way to prevent Hepatitis B is by getting vaccinated, and it is recommended that all children from 12 months of age should be given this vaccine, except high risk infants to whom it should be given at birth.
When travelling to areas where Hepatitis B and D infections are common, get vaccinated before the trip. For more information on travel vaccination please visit: https://deputyprimeminister.gov.mt/en/phc/pchyhi/Pages/Travel-Vaccination.aspx.
Other preventative measures include:
- Never sharing needles or other items with other intravenous drug users.
- Not sharing personal care items, like toothbrushes or razors.
- Condom use in the case of sexual activity with multiple partners.
- Use of gloves, face masks and eye shields in the case of healthcare providers.
- Seeking medical help immediately if there was possible exposure to Hepatitis B infection.
Vaccines available in Malta
Click here for more information on vaccination.
Support and Contacts for further information contact
- Your GP (family doctor).
- The Genito-Urinary (GU) Clinic on 25457494/1.
- The Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Directorate on 23266000.
- The Detox helpline 22261800.
- Floriana Immunisation Centre: 25680222/3/4-25680000.
Resources List:
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b
https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/index.htm
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-d