Hepatitis C
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. There are different types of Hepatitis, but this fact sheet will only focus on Hepatitis C.
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the Hepatitis C virus. It can be acute or chronic. Persons who have been infected for less than 6 months are suffering from Acute Hepatitis C. They generally show no symptoms. Approximately 20% of infected persons will clear the virus within 6 months and will have no long-term consequences. The remaining 80% of infected persons will develop chronic Hepatitis C. Such infected persons will carry the virus for the rest of their lives and will remain infectious and at risk to others.
What are the symptoms of Hepatitis C?
You may have no symptoms and do not know that you are infected. If symptoms occur, at first they may be similar to flu sickness.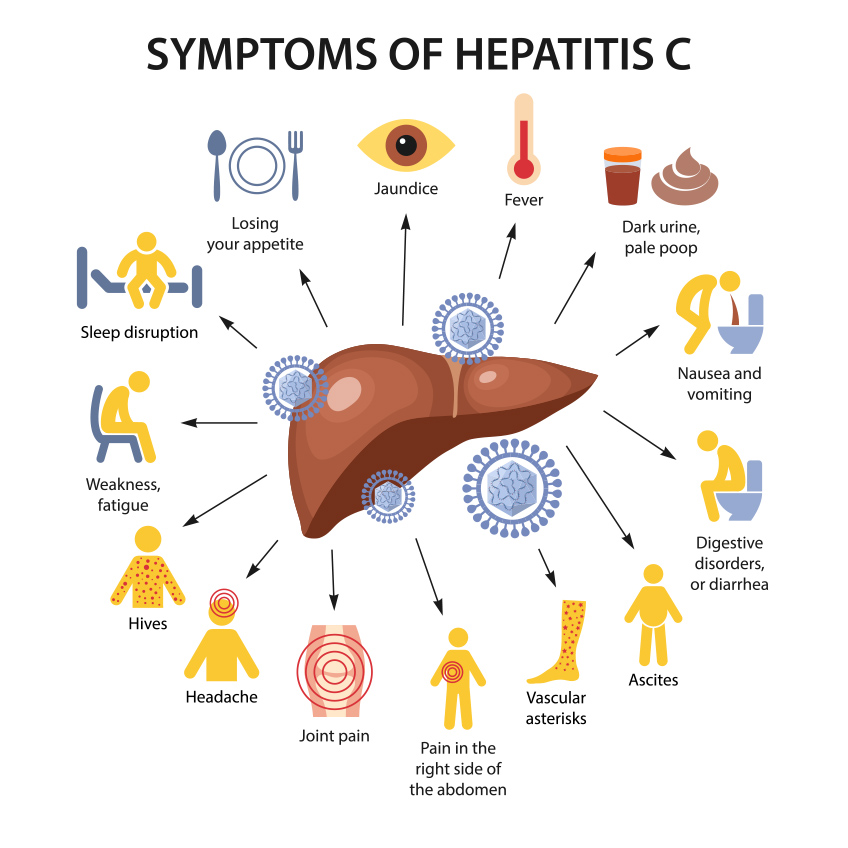 When do symptoms occur?
When do symptoms occur?
Most cases have no symptoms. The symptoms appear anytime between 2 weeks and 6 months after infection. However, symptoms may develop many years later with the possibility that the damage to liver would be already in the advanced stage.
Are there different types of Hepatitis C?
Yes, there are 4 types of Hepatitis C virus known as genotypes. Your doctor will guide which virus you are infected after a blood test.
How is Hepatitis passed on?
The hepatitis C virus is passed from one person to another mainly through blood that is infected.
High risk activities include:
- Sharing of drug-injecting equipment (needles, heating spoons and snorting equipment). This is the most common way how people become infected.
- Using non-sterilised equipment for tattooing, acupuncture or body piercing (it is important to go to a Public Health registered outlets).
Medium-Low risk activities include:
- Sharing or not disposing of grooming and hygiene supplies like shaving razors and toothbrushes of infected persons.
- Exposure to blood during unprotected sex with an infected person. Sexual transmission is an uncommon way of becoming infected with Hepatitis C. However, there is research showing that men who have sex with men (MSM), who are HIV-positive, and have multiple sex partners have an increased risk for Hepatitis C.
- Needle stick injuries in health care settings.
- Poor infection control: contaminated and inadequately sterilized equipment used in medical and dental procedures.
- Rarely from an infected mother to baby during childbirth.
How is Hepatitis C not passed on
Hepatitis C is only transmitted through infected blood. It is not passed on from kissing, hugging, shaking hands, eating from same plate or drinking from same glass.
Can Hepatitis be treated?
Yes! Over 90% of Hepatitis cases can be treated and cured. New and improved treatments with minimal side effects and toxicity are locally available. All information regarding treatment can be discussed with your doctor.
How can Hepatitis C be prevented?
There is NO vaccine to prevent Hepatitis C but there are always ways of how to reduce the risk of getting infected:
- Do not share needles, spoons or snorting practices for drug use.
- Avoid sharing shaving razors, toothbrushes or other personal belonging that involves contact with infected blood.
- Always use condoms for sexual encounters.
- Attend to licensed tattooing, acupuncture or body piercing parlours.
Support and Contacts
- Your General Practitioner (Family Doctor).
- GenitoUrinary (GU) clinic 25457494/1.
- Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Directorate 23266000.
- Detox helpline 22261800.
Reference List:
https://www.cdc.gov/knowmorehepatitis/media/pdfs/FactSheet-Boomers.pdf
https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/resources/professionals/pdfs/CounselingandTestingPC.pdf